|
Home  Team Team  Contact us Contact us |
| About us | Our activity | Highlights | Publications | Gallery | New events |
| RE-doped nanocrystals | J-aggregates | Cell marking | Inorganic synthesis | Organic synthesis |
 |
 |
 |
Our results:
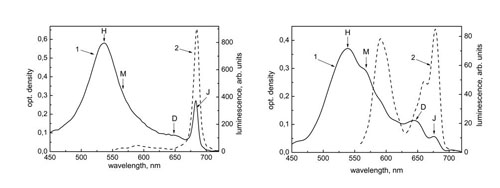
Optical spectroscopy experiments were used to study the features of cyanine dye 3,3’-dimethyl-9-(2-thienyl)-thiacarbocyanine iodide (L-21 (J6)) aggregation in binary solutions DMF:TRIS-HCl buffer (pH = 8) containing nucleic acids (DNA or RNA). The appearance of absorption and luminescence bands associated with J-aggregates and dimers that are formed within the minor groove of DNA has been observed. The model of L-21 J-aggregate structure is proposed. It has been found that dimers are the building blocks of L-21 J-aggregates. Disorientation in dimers caused by the minor groove curvature is reason of observation of Davydov splitting in absorption spectrum of L-21 J-aggregates. In the solution containing DNA the absorption and luminescence bands of L-21 J-aggregates exhibit the specific properties that allows the dye L-21 to be used as a fluorescent probe for DNA detection.
Absorption (1) and luminescence (2) (excited at 530 nm) spectra of L-21 (0.1 mM) in a binary solution DMF:TRIS-HCl buffer with DNA (left) and RNA (right).Main publications:
• G.Ya. Guralchuk, A.V. Sorokin, I.K. Katrunov, S.L. Yefimova, A.N. Lebedenko, Yu.V. Malyukin, S.M. Yarmoluk. Specificity of cyanine dye L-21 aggregation in solutions with nucleic acids // J. Fluorescence – 2007. – v.17, ¹ 4. – P. 370-376. abstract
to the top